A healthy amount of zinc in your diet can do wonders for many aspects of your health. Zinc is essential for hundreds of the body’s functions and systems. The body cannot make zinc, so it is necessary to regularly introduce it through food. Zinc is important across all life stages, from supporting growth in childhood to playing a role in immunity and healthy ageing.
What is the role of zinc?
Zinc is needed for the activity of numerous enzymes and proteins and is essential for the creation and protection of DNA. It’s found throughout the cells of the body and helps them to grow. It’s super important for healthy functioning of the immune system and for tissue regeneration and repair.
5 key body benefits of zinc
Here are 5 powerful zinc benefits that you might not know about:
- Growth and development – Because of its role in helping cells grow and multiply, zinc is especially required in times of rapid growth including pregnancy and throughout childhood and adolescence. When kids don’t get enough zinc through their diet, it can impair their growth and development.1
- Immune health – Zinc plays a central role in the function of the immune system and keeping us well. It’s crucial for the normal development and function of white blood cells including neutrophils, macrophages and natural killer cells, which provide a first line of defence against pathogens that can make us ill.2 Zinc also supports the activity of immune cells that produce antibodies against invading pathogens.2 One study found that taking a zinc supplement can shorten the duration of the common cold by over 2 days in healthy adults.3 When the body doesn’t get the zinc it needs, it can impair immune system function and increase susceptibility to various infections.1 The Ethical Nutrients Immune Health range has a variety of products containing zinc that help keep you strong at various stages of infection.
- Wound healing – Zinc plays a major role in the wound healing process as it’s required for collagen and protein synthesis, cell multiplication, the inflammatory response and the function of white blood cells that help to clean up, fight infection and support healing.4
- Healthy skin – Zinc encourages the production of collagen and elastin and supports the structure of the skin. It has antioxidant effects, supports tissue repair and plays a role in the inflammatory process.5 Zinc might be useful for relieving symptoms of acne and soothing skin inflammation in teenagers as well as supporting healthy skin aging in mature adults. Ethical Nutrients Healthy Hair, Skin & Nails combines zinc with other skin-fluencing ingredients such as silicon, biotin & selenium to keep skin, nails & hair healthy.
- Male reproductive health – Men require a higher daily intake of zinc than women to support normal testosterone levels, a healthy prostate and sperm production.6
What happens if I don’t get enough zinc?
Zinc deficiency has a number of negative effects on health across all ages and stages of life. If kids are zinc deficient, it can slow their growth, diminish their appetite and increase their susceptibility to frequent infections. If adults don’t consume enough zinc, it can lead to immune system deficiencies, hair loss, impaired wound healing and affect their taste and sense of smell. In mature individuals, zinc deficiency can delay wound healing and cause problems with thinking, reasoning and memory.7
Unfortunately, mature adults, especially men, are at a higher risk of zinc deficiency. Research shows that an estimated 15% of men aged over 50 and 30% of men aged over 70 are considered to be zinc deficient.8 Other groups at risk of low zinc levels include pregnant and breastfeeding women who have higher zinc requirements to support the growth and development of their baby, along with vegetarians and vegans because the body finds it harder to absorb zinc from plant sources compared to animal products.4
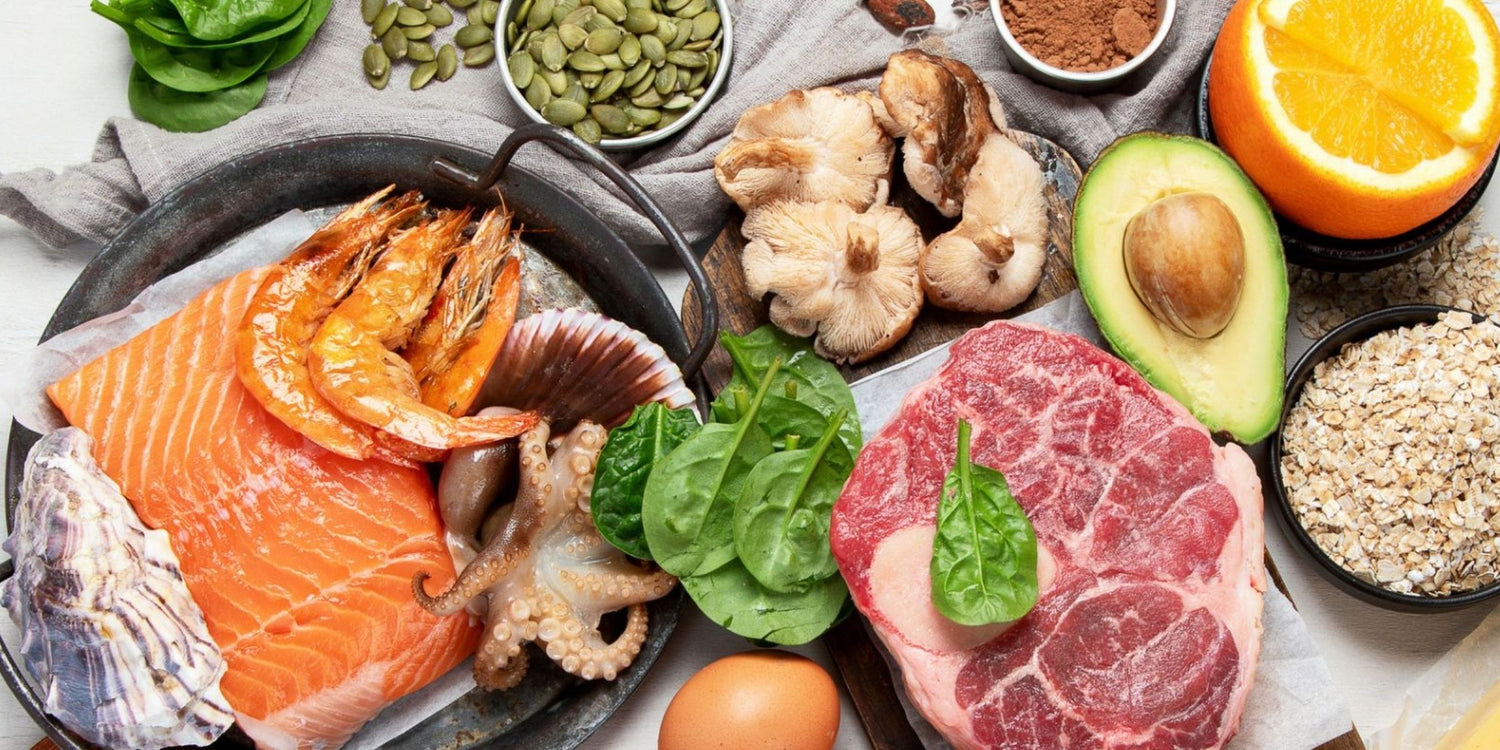
Foods high in zinc
You can get your recommended intake of zinc by consuming a variety of zinc-rich foods including:1
- Oysters, which are packed with zinc
- Beef, crab, turkey, pork and chicken
- Nuts and seeds such as pinenuts, cashews, sunflower seeds, pecans and almonds
- Cheddar cheese, yoghurt and cow’s milk
- Chickpeas and soybeans
- Whole grains
Do I need a zinc supplement?
Sometimes you might need more zinc than you can get from food alone. Zinc supplements may be appropriate:
- For people wanting to support the body’s immune defences throughout winter, or all year round
- In supporting healthy skin, soothing skin inflammation and relieving symptoms of mild acne in teenagers
- In children who might be fussy eaters to support their growth and development and for their general immunity
- For men wanting to support a healthy reproductive system
- In mature adults who are at risk of deficiency to support wound healing and immune system function
- For people following a vegan, vegetarian or plant-based diet
The Ethical Nutrients Mega Zinc range provides zinc on its own or in combination with other useful vitamins and nutrients such as vitamin C. These are available in a variety of different forms, including powders and tablets to suit your unique needs. We only use Meta Zn® (zinc diglycinate) in our zinc supplements, which is a high quality zinc with enhanced absorption so you can get the most from supplementation.
References
- Higdon J, 2019, Zinc, Linus Pauling Institute, viewed 6 June 2023, <https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/minerals/zinc#reference63>
- Prasad, AS et al, 2008, ‘Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells’, Molecular medicine, vol 14, no 5-6, pp 353-7
- Wang, MX et al, 2020, ‘Zinc Supplementation Reduces Common Cold Duration among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials with Micronutrients Supplementation’, Am J Trop Med Hyg, 103, no 1, pp 86-99
- Harvard School of Public Health, 2023, Zinc, viewed 6 June 2023, <https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/zinc/>
- Gupta M et al, 2014, ‘Zinc therapy in dermatology: a review’, Dermatol res prac, vol 2014, no 709152
- Fallah A et al, 2018, ‘Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men's Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization,’ J reprod infertile,vol19, no 2, pp 69-81
- National Institutes of Health, 2022, Zinc, viewed 6 June 2023, <https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-Consumer/>
- Beckett J et al, 2015, ‘Zinc status of northern Tasmanian adults’, J Nutr Sci, vol. 4